SSH, or Secure Shell, is a powerful tool for managing your website remotely from a secure server. You can use different commands through a terminal interface to perform various tasks without having to open your site’s backend.
Although SSH is typically used by more advanced WordPress users, it can also be a huge help if you can’t get into your WordPress admin area.
In this article, we will show you some SSH commands that every WordPress user should know.
Here are all the topics and commands we will cover in this guide. You can click the links below to jump ahead to any section:
What Is SSH?
SSH, short for Secure Shell, is a secure protocol for running your website using a command-line interface. It lets you connect your computer to your site’s server.
The best part about using SSH is that it lets you access your WordPress site from a remote server. You don’t have to open the WordPress dashboard.
Simply write different commands to perform tasks like installing WordPress, transferring files, creating directories, and more.
Using SSH is meant for more technical users or developers who want to execute commands.
However, other users can also use SSH to access their site in case something goes wrong and they can’t open the WordPress admin.
Expert Tip: Locked out of your WordPress site and don’t know what to do? Our team of professionals can help you regain access in no time. Check out our WPBeginner Premium Support Services today!
That said, let’s first look at how you can use SSH to connect to your site’s server.
How to Connect to Your WordPress Site Using SSH
The first thing you need to do is check whether SSH is installed on your site server.
Since SSH is a client-server technology, you can check if it’s configured by contacting your WordPress hosting service, and they can tell you. Or you can try accessing the cPanel or hosting dashboard.
You should find something that looks like the image below:
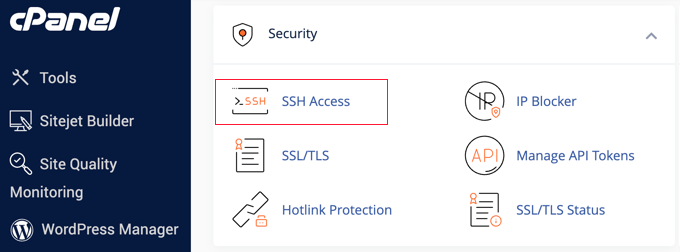
Next, you will need to note down the IP address, username, password, and port. This information will be needed when you use SSH to connect your site from your computer.
Using SSH on a Mac or Linux Computer
If you’re using a Mac or Linux operating system, then you can simply connect to your site using the terminal app.
Go ahead and enter the following command in the terminal:
ssh username@server_ip_address
Just replace the username and server_ip_address with the information of your hosting provider.
Using SSH on a Windows Computer
To use SSH and connect to your site on a Windows machine, you will need a third-party tool like PuTTY.
Once you download and install the application, you will need to enter the host name (IP address) and port number you noted above to connect to your site.
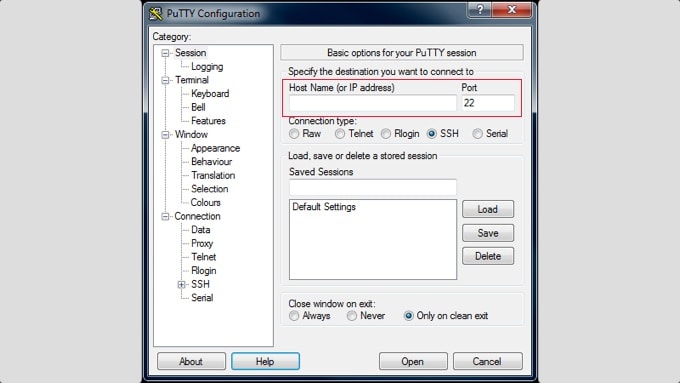
After entering these details, click the ‘Open’ button. In the next step, a terminal window will open where you can simply enter the username and password to access your site.
Now, let’s look at some common SSH commands every WordPress user should know.
SSH Commands for Basic Navigation
You can use different SSH commands to navigate your way around files and directories. Here are some basic navigation commands you should know.
1. pwd – Shows Full Path to the Directory
The pwd command displays the full path to the current directory. This is really useful for navigating between different files and folders:
Since you don’t get any visual references to pinpoint where you are currently on the server, you can simply use this command to find your way.
2. ls – Lists Files and Folders in a Directory
If you want to view the contents of a directory, then you can simply use the ls command.
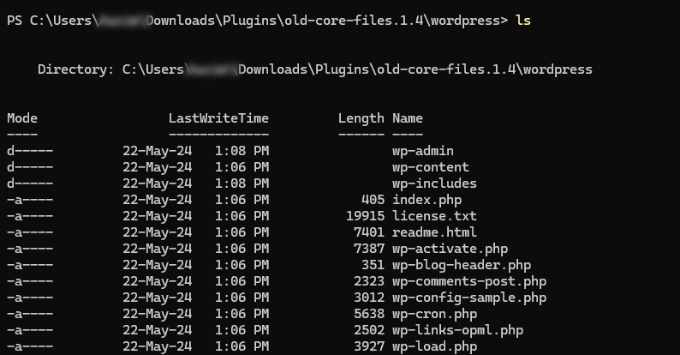
You can also use additional parameters to get more information about the content. For example, simply add -l for detailed information or -a to show hidden files.
3. cd – Change Directory
The cd command lets you change directories. You can move to a subdirectory or an entirely different directory:
In the above code, you can replace [directory] with the name of the directory.
For instance, if you enter thecd wp-content/themes command, then it will move you to the themes directory within your WordPress installation.
SSH Commands for File and Folder Management
Next, let’s look at some SSH commands for managing files and folders on your WordPress website server.
4. mkdir -Create a New Directory
Using the mkdir command, you can create a new directory in the current directory. Simply enter the following command along with the name of the folder:
For example, let’s say you want to create a folder for stylesheets. The SSH command for this will be mkdir stylesheets.
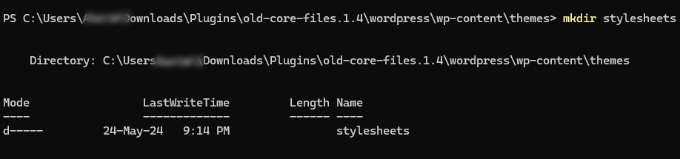
On the other hand, if you want to create a new directory that is within another subdirectory, then you’ll need to enter the structure along with the mkdir command.
Here’s what the syntax will look like:
mkdir /plugins/myplugin/stylesheets
5. rmdir – Remove Empty Directory
You can use the rmdir command to delete a directory from your site’s server. All you have to do is enter the command followed by the directory name:
Important Note: Be careful when using this command. Once a directory is removed from the server, you cannot undo it.
6. cp – Copy a Folder or File
The cp command lets you copy a file or folder to another location. When entering the command, you’ll need to specify the name of the file or folder and the destination where the copy will be saved:
cp [file name] [destination]

When entering the file name, you will also need to include the file extension, such as examplefile.txt or readme.html.
If you want to make a copy of the file in the same folder, then you can enter the following command:
cp readme.html readme2.html
If you want to copy a file to a different folder, then you’ll need to enter the following command:
cp /public_html/wp-content/readme.html /public_html/etc/
You can also use different parameters with the cp command, like:
cp -rcopy all the content of a foldercp -aarchive all the filescp -uoverwrite a file in a destination folder only if it contains new or different contentcp -nwon’t copy a file if it already existscp -ishows a warning before copying a filecp -freplaces or removes a file from the destination folder if there is another file with the same name
7. mv – Moves a File or Folder
If you want to move a file or folder to a new destination, then you can use the mv command.
Just like using the cp command, you will need to specify the file name and destination where you’d like to move the file:
mv [file name] [destination]

For example, let’s say you want to move an ‘index.php’ file to the stylesheets folder. In this case, the command should be:
8. grep – Look for a Specific Phrase
Next, you can use the grep command to search for a specific phrase or string in a file. Do note that this command is case-sensitive.
Here’s what the syntax would look like:
grep '[search phrase]' [file name]

For example, let’s say you want to find the term ‘header’ in the info.txt file.
In this case, the command would look like this:
Besides that, you can also use the -i parameter to ignore letter cases when performing the search.
9. find – Search Files and Directories
If you’re looking for a specific file or directory, then you can use the find command and search for file name, size, file type, and more.
The syntax for the find command looks like this:
find [starting directory] [parameter] [search term]
In the code above, you can specify the search process.
For example, here are some options to choose from:
- / (slash) – This lets you search the entire system
- . (dot) – You can search the working directory
- ~ (tide) – This searches the home directory
Next, the SSH command also lets you specify the parameters, like name, size, file type, and more.
-name– Looks for file name-user– Searches for files assigned to a given user-size– The file size-type -d– Looks for a directory type-type -f– Looks for a file type
Lastly, you can enter the search term you’re looking for. Let’s say you want to find a file named ‘task’ in the directory.
The SSH command for this would be:
Other Useful SSH Commands
Now that you know some basic SSH commands for navigation and managing the files and folders on your site, here are some additional commands you should know about.
10. zip – Compress a Folder
If you’re looking to compress large files or folders, then you can use the zip command. All you have to do is include the name of the file or folder you want to compress:
zip filename.zip foldername
You can also use different parameters with this command to specify whether you’d like to delete the original folder:
zip -r filename.zip foldername– This compresses a folder but doesn’t delete itzip -m filename.zip foldername– You can use this parameter to compress a folder and then delete it, leaving you with just the zipped versionzip -d filename.zip foldername– Use this to delete a file from the existing zip archivezip -u filename.zip foldername– This updates a file within an existing zip archive. It is helpful if you’ve updated the original file and don’t want to delete the zip file or create a new one.
11. unzip – Decompress a Folder
After zipping a folder, you’ll need to unzip it as well. For this, go ahead and simply enter the unzip SSH command:
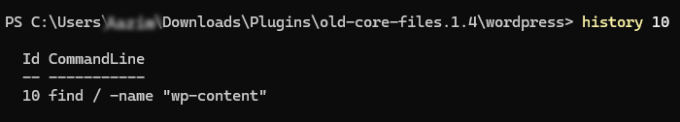
12. history – View Last Used Command
The history SSH command is useful for determining which command you entered previously. Be sure to enter a number to limit the displayed results.
For example, let’s say you want to see the last 10 used commands. The syntax for the history command looks like this:
13. tar – Create and Unpack Compressed Archives
tar is a popular SSH command used to unpack .tar.gz files. There are many third-party tools that use this format to compress files, and it is an alternative to zip files.
If you want to archive a folder, then you can use the command below. Simply replace ‘archivename.tar.gz’ with the file name and ‘directory’ with the path of the directory:
tar -cvzf archivename.tar.gz directory
After archiving, you can unpack the .tar.gz file using this command:
tar -xvzf archivename.tar.gz directory
14. clear – Remove All Text
You can use the clear command to remove all text from the terminal window:
This command is useful if you have made an error or want to start fresh.
15. du – View File or Folder Size
If you want to know the size of a file or folder on your WordPress server, then you can use the du command:
du -h [file or folder name]
The -h parameter in the code shows the file size in human-readable format.
For example, let’s say you want to view the size of the .htaccess file.
All you have to do is enter this command:
16. exit – Exits the Remote Site Server
After you’re done working on your WordPress site and want to exit the remote server, then you can simply type in the exit command:
We recommend using this command every time you connect to your site. This way, no one else will be able to access your server using SSH after you’ve finished working.
We hope this article helped you learn important SSH commands that every WordPress user should know. You may also want to see our guide on common WordPress errors and how to fix them or how to troubleshoot WordPress.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
این خبر را در ایران وب سازان مرجع وب و فناوری دنبال کنید
